
Carbon Nanotube FET Mixers and High Frequency Applications
Abstract

A Carbon Nanotube Field Effect Transistor refers to a FET that utilizes a single CNT or an array of CNT’s as the channel material instead of bulk silicon in the traditional MOSFET structure. Field-effect transistors (FETs) based on moderate or large diameter carbon nanotubes (CNTs) usually suffer from ambipolar behavior, large off-state current and small current on/off ratio, which are highly undesirable for digital electronics. To overcome these problems, a feedback-gate (FBG) FET structure is designed and tested. Carbon nanotube field-effect transistors (CNFETs) are a promising nanotechnology for the development of energy-efficient computing. Despite rapid progress, CNFETs have only been fabricated in.
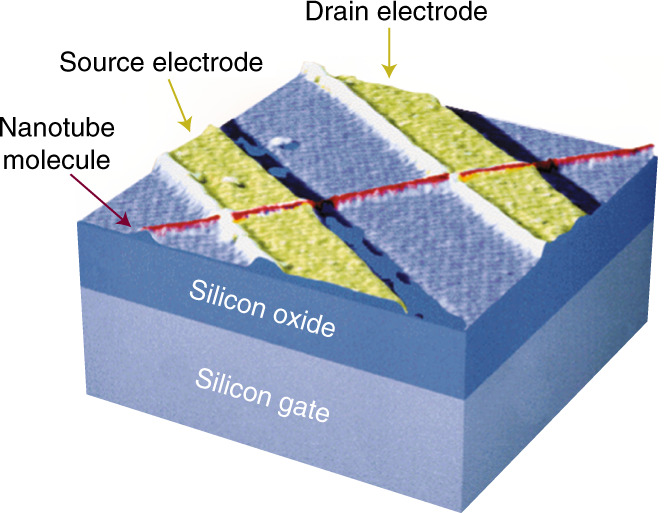
Cnt Transistor
We have investigated the high frequency electrical properties of single-walled carbon nanotube field effect transistors by operating the devices as microwave mixers. The mixing current amplitude depends linearly on the transconductance and quadratically on the applied AC voltage. On devices with insulating substrates, the response is approximately independent of frequency up to 40 GHz. Two applications of these high frequency-operation carbon nanotube FET mixers will be discussed: the detection of terahertz electrical pulses and nanoscale dielectric spectroscopy of liquids.
Carbon Nanotube Fetal Alcohol Syndrome

Carbon Nanotube Feta
- Publication:
- Pub Date:
- March 2007
- Bibcode:
- 2007APS..MARS28004Z
